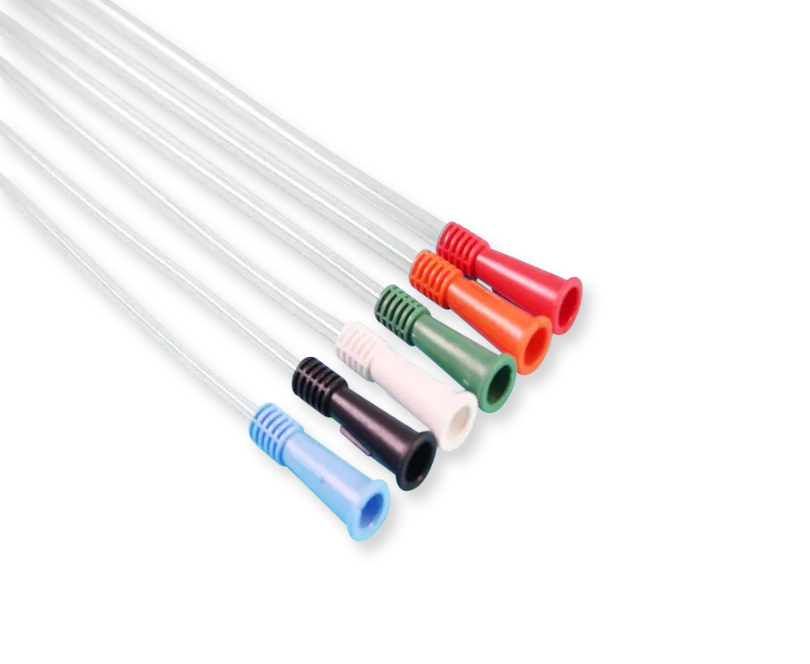
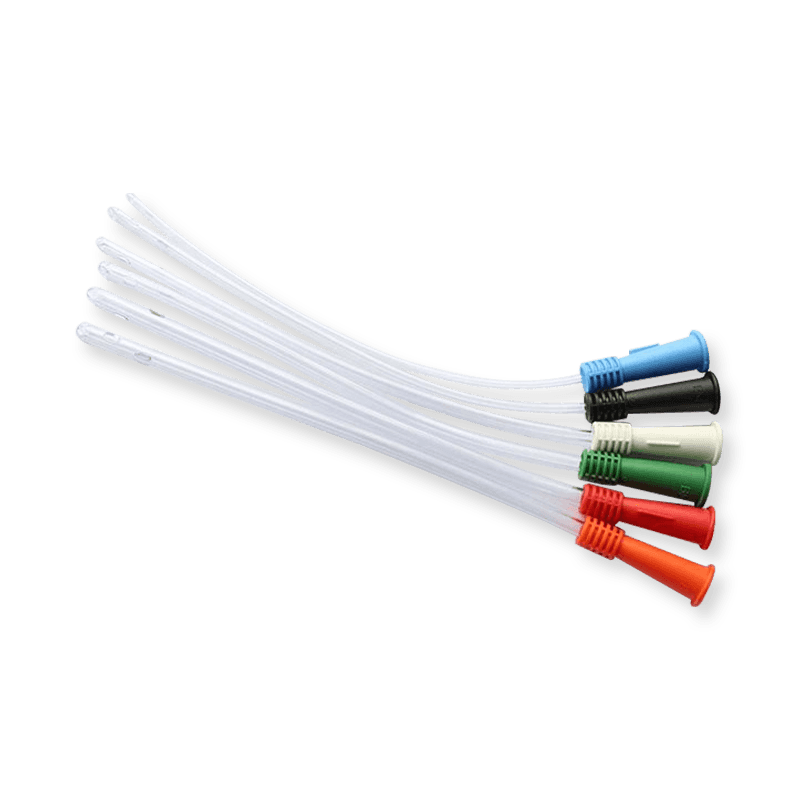
The coude tip catheter, designed with a curved tip, is specifically tailored for male urethral anatomy. Because the male urethra is relatively long and curved, straight catheters can be challenging to pass and may cause discomfort. When a coude tip catheter can be inserted into the bladder, a balloon-tipped coude tip catheter, such as a Foley catheter, may be used if prolonged catheterization is required. Additionally, if a straight catheter cannot be used to access the bladder in female patients, the angled tip of a coude tip catheter may be employed to irrigate blood clots within the bladder. Coude Tip Male Intermittent Catheter How to Insert a Coude Catheter Inserting a coude catheter is a common medical procedure often performed by healthcare professionals to relieve urinary retention or facilitate bladder drainage. This guide provides a detailed overview of the steps involved in the insertion process, as well as important precautions. I. Preparation Understand Indications: Coude catheters are typically used for patients with anatomical abnormalities, enlarged prostates, or strictures that may obstruct standard catheterization. Gather Supplies Coude catheter (select appropriate size and type based on patient needs) Sterile catheterization kit (includes sterile gloves, antiseptic solution, lubricant, cotton balls, etc.) Underpad or urinal Waste disposal bag (for disposing of medical waste) Hand Hygiene: Thoroughly wash your hands to reduce the risk of infection before handling any medical instruments. Inform the Patient: Explain the procedure to the patient, including its purpose and steps involved. Ensure that you obtain informed consent. II. Insertion Steps Patient Positioning: Position the patient comfortably, usually in a supine position. Ensure privacy with appropriate draping. Aseptic Technique: Clean the insertion site using an antiseptic solution. For females, clean from front to back; for males, clean the glans penis in a circular motion. Wear Sterile Gloves: Put on sterile gloves to maintain a sterile environment while handling the catheter. Lubricate the Catheter: Apply a generous amount of sterile lubricant to the tip of the coude catheter to ease insertion. Insert the Coude Catheter: For Females: With one hand, gently separate the labia, and with the other hand, insert the coude catheter into the urethra at a slight upward angle. Advance the catheter until urine flows, usually about 5-7 cm deep. For Males: Hold the penis at a 90-degree angle to the body. Insert the coude catheter gently into the urethra, advancing to a depth of about 15-20 cm, or until urine flows. Secure the Catheter: Once urine flows, secure the catheter to the patient’s thigh using adhesive tape or a catheter strap to prevent movement. Collect Urine: Connect the catheter to a drainage bag to collect urine. Ensure the bag is positioned lower than the bladder to facilitate gravity drainage. Clean Up and Document: Remove gloves and perform hand hygiene again. Dispose of all waste materials properly. Document the insertion time, depth, catheter type, and any observations regarding the patient's response. III. Precautions Monitor Patient Response: Throughout the procedure, observe the patient for signs of pain or discomfort. If significant discomfort occurs, stop the procedure and reassess. Infection Prevention: Maintain strict aseptic technique to minimize the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs). Routine Catheter Care: Follow facility protocols for routine catheter care and maintenance. This includes regular assessments and changing the catheter as needed, usually every 2-4 weeks. Patient Education: Provide the patient with information on how to care for the catheter, including maintaining catheter patency and monitoring urine output. IV. Conclusion The insertion of a coude catheter is a routine yet critical procedure that requires skill and attention to detail. By following established protocols and maintaining a sterile environment, healthcare providers can effectively minimize complications and ensure patient comfort. Should any challenges arise during the procedure, do not hesitate to consult with experienced colleagues or supervisors for assistance. Proper training and adherence to best practices are essential for successful catheterization and patient safety. Coude catheters play an essential role in urological care, particularly for patients facing challenges with standard catheters. Their unique design enhances patient comfort and treatment efficacy. If you need specific information from a website or further details about a particular aspect, please contact us or log on the website (www.bevermedical.com)
View More +-
04 Nov 2024
Urinary incontinence affects people of all ages worldwide, with a higher prevalence as age increases. And women are more likely to experience urinary incontinence than men. To maintain a normal social life, patients often choose a suitable catheter according to the suggestions. As we know, most intermittent catheter users apply lubrication before inserting the catheter to reduce discomfort. Luckily, a hydrophilic intermittent catheter brings great ease to patients, because it doesn’t require additional lubricant. In this article, you'll get to know complete information on hydrophilic catheters, including types, advantages, and guides. What Is a Hydrophilic Catheter? A hydrophilic catheter has a layer of hydrophilic polymer coating wrapped around the PVC catheter, also called a super-smooth catheter. When this catheter comes into contact with water or urine, the coating attracts water molecules and becomes very slippery, allowing it to easily glide into the urethra. This reduces friction between the catheter and the urethral lining, helping to minimize the risk of urethral damage. Additionally, the coating is safe and hypoallergenic, making it suitable for daily use in continence care. Types of Hydrophilic Catheters Hydrophilic catheters mainly come in two types: 1. Dry Coating Catheters – These remain dry until activated with water. Before insertion, the catheter needs to be soaked in water to activate the hydrophilic coating. 2. Pre-Lubricated Catheters – These come in a water-filled package with the hydrophilic coating already activated. You simply open the package, and the catheter is ready for immediate use. Who Benefits Most from Hydrophilic Catheters? 1. People Needing Intermittent Self-Catheterization For patients who need to use a catheter several times daily, hydrophilic intermittent catheters help reduce irritation, infection risk, and discomfort. 2. People with High Sensitivity If patients are more sensitive to pain and benefit from the lubricating effect of hydrophilic catheters, it can help make insertion more comfortable. 3. People Experiencing Discomfort with Self-Catheterization Repeated self-catheterization can cause urethral damage if improperly lubricated. Hydrophilic catheters are smoother, reducing friction and discomfort. 4. Others Anyone can benefit from the ease and comfort of a hydrophilic catheter. Benefits of Using Hydrophilic Catheters 1. Easy to Use Without Extra Lubrication Hydrophilic catheters eliminate the need for separate lubrication, saving time and making the process easier and more comfortable. 2. Convenient and Ready-to-Use Most hydrophilic catheters come with their own sterile water, making them more practical, especially when using a public restroom. 3. More Hygienic Since no external lubricant is needed, the chance of accidental contamination is reduced, lowering the risk of infection. 4. Less Urethral Trauma The hydrophilic coating is smooth and even along the entire catheter, unlike non-coated catheters where lubrication might be inconsistent. This coating reduces friction and minimizes the risk of urethral damage. How to Use a Hydrophilic Catheter 1. Hand Washing Thoroughly wash your hands before starting to reduce infection risk. 2. Activate the Hydrophilic Coating Hydrophilic catheters are usually pre-packaged with sterile water or include a separate water packet. If it has a water packet, apply pressure (often by pressing with your palm) to break the packet, allowing water to cover the catheter. Gently shake to ensure full coverage of the catheter. Some brands offer hooks or tape to hang the catheter for 30 seconds to allow full hydration and activation of the coating. If not, hold the catheter upright for the same time to ensure maximum smoothness. 3. Insert the Catheter For Women – Find a comfortable sitting or standing position and locate the urethral opening with a mirror. Slowly insert the catheter approximately 3 inches (7.5 cm) until urine begins to flow. Push in about another inch (2.5 cm) to ensure proper positioning in the bladder. For Men – Slowly insert the catheter into the urethral opening. Once urine flows, push it in about an inch (2.5 cm) further to ensure it reaches the bladder. What to Do After Using a Hydrophilic Catheter? 1. Empty the Bladder – Once inserted, the urine will start to flow naturally. Allow the bladder to fully empty until no more urine comes out. 2. Remove the Catheter Gently – Once done, slowly remove the catheter from the urethra, avoiding sudden movements to reduce irritation. 3. Dispose of Single-Use Catheters – Safely discard single-use hydrophilic intermittent catheters in a medical waste bag. 4. Wash Hands – Must wash your hands thoroughly to maintain good hygiene and prevent infection. Conclusion Hydrophilic catheters offer significant benefits despite being more costly, especially for those who need intermittent catheterization. If you’re considering a hydrophilic intermittent catheter, consult your doctor or healthcare provider first. Then, contact Bever Medical, we can provide quality and safe catheterization products. We offer OEM services and have the expertise to help you with any concerns.
View More + -
14 Nov 2024
Are you considering Coudé catheters to make your life better? I must say, it's a good choice. It features a slightly angled or curved tip, making it particularly suitable for patients who encounter difficulties with standard straight catheters. If you're looking for a comfortable solution, you've come to the right place. With Bever Medical, getting to know about the differences between straight tip and Coudé tip catheters, will help you make an informed decision. About the Coudé Catheter Typically, catheters come in two tip options: straight and Coudé. While a straight tip is generally usable, the Coudé tip more easily navigates urethral strictures or other obstructions. Straight Tip Catheter A straight tip catheter is a thin, straight tube used for quick bladder emptying. Its flexible structure and end-hole design help guide urine into the toilet. These single-use catheters come in a variety of sizes and features to meet different needs, including pre-lubricated hydrophilic options, hypoallergenic materials, and latex options. There are also portable, bagged catheters for discrete use and on-the-go convenience. Straight Tip Female Intermittent Catheter Advantages Easy to Insert: With a fully straight tip, straight catheters are often easy to insert when there are no obstructions. Affordable and Cost-Effective: Straight catheters are generally lower in price, especially when purchased from Bever Medical. Suitable for Home Use: Straight catheters are ideal for self-use by both men and women and often do not require assistance from healthcare providers (unless insertion difficulties arise). Disadvantages Straight catheters may cause discomfort during insertion, especially if insertion is forced, which can increase the risk of injury. They require careful cleaning, and carrying them around discreetly can be challenging. Some users experience pain (if pain or discomfort occurs, consult a doctor who may recommend a Coudé catheter for added comfort). How to Insert a Straight Tip Catheter? 1. Preparation Wash your hands thoroughly and prepare all necessary catheter supplies. Men usually stand or sit over the toilet, while women may use a standing or foldable mirror for better visualization of the urethral opening. 2. Cleaning Ensure the genital area around the urethral opening is clean. A topical anesthetic can be applied if recommended by your doctor, with a wait of about one minute for it to take effect. 3. Insertion Men should hold the penis in one hand and slowly insert the catheter tip into the urethra. Women can sit on the toilet, use one hand to separate the labia, and with the other hand, guide the catheter into the urethra. 4. Emptying the Bladder Keep the catheter in place until urine flow stops. 5. Removal and Cleaning Gently remove the catheter, dispose of it appropriately, wash your hands, and clean the area. Coude Tip Intermittent Catheter What is a Coudé Tip Catheter? The Coudé tip catheter has a slightly curved tip near the end, which helps it bypass narrow areas or blockages in the urethra. The term “coudé” comes from the French word for "bent" or "elbow." Coudé catheters are available with three different tip styles: tapered, Tiemann, and olive tip. Compared to straight catheters, the unique curved design of a Coudé catheter allows it to glide more comfortably past narrow urethras or enlarged prostates. For patients who experience discomfort with straight catheters, urologists may recommend a Coudé tip catheter. Advantages The curved tip of the Coudé catheter helps avoid irritation of sensitive tissues, reducing discomfort during insertion. It's easier to maneuver around obstacles such as an enlarged prostate or urethral strictures. The angled tip allows the user to have more control over the catheter direction, reducing the risk of unintended injury. Disadvantages Compared to straight catheters, Coudé catheters are often more costly because of their specialized design. They require training and practice to prevent improper insertion and potential injury. If not handled properly, the curved portion of the Coudé tip can increase the risk of tissue damage, especially in sensitive areas. How to Insert a Coudé Tip Catheter? The inserting steps are similar to a straight catheter, but with added care for the Coudé catheter’s angled tip. If you find it challenging initially, seek help from a urologist or healthcare provider. Straight Tip vs. Coudé Tip Catheters Both the Straight Tip and Coudé Tip catheters have distinct advantages depending on your needs. If you experience blockages, urethral strictures, or discomfort with a straight catheter, you can use a Coudé catheter. If you're unsure, you can consult a medical professional who can provide the best advice for your situation. Where to Obtain Coudé Catheters? You can get them online or offline, there are many brands and types of Coudé catheters for your consideration. But do remember to follow your doctor’s suggestion. Catheter use should be comfortable, therefore, you can get them at Bever Medical. It offers high-quality straight tip and Coudé tip catheters, both of which are made of safe, comfortable materials. If you need any urological supplies, feel free to reach out to us.
View More + -
22 Nov 2024
Intermittent catheters are widely used by men who need assistance draining their bladder due to conditions like urinary retention, neurogenic bladder, or post-surgical recovery. These catheters are temporary, single-use devices that offer flexibility, safety, and control over bladder management. For men, intermittent catheters come in various designs and materials to accommodate individual anatomy, preferences, and specific medical requirements. Below is a detailed overview of the different types of intermittent catheters for men and their unique features. 1. Straight Tip Intermittent Catheters Straight tip catheters are the most basic type of intermittent catheter. As the name suggests, they have a straight, smooth tip and are inserted through the urethra into the bladder to drain urine. Key Features: ·Simple Design: Easy to use and widely available. ·Cost-Effective: Typically less expensive than specialized catheters. ·Material Options: Available in latex-free materials such as silicone or PVC to reduce the risk of allergies. Best For: ·Men with no significant obstructions in the urethra. ·Patients new to catheterization or with straightforward needs. 2. Coude Tip Intermittent Catheters Coude tip catheters are characterized by a slightly curved or angled tip, designed to navigate around anatomical obstructions, such as an enlarged prostate or urethral strictures. Coude Tip Male Intermittent Catheter Key Features: ·Curved Tip: Easier insertion for men with urinary tract blockages. ·Directional Marking: Some coude catheters have markings on the hub to indicate the position of the angled tip during insertion. ·Material Variants: Available in flexible silicone or firmer materials for better control. Best For: ·Men with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). ·Patients with urethral scarring or strictures. 3. Hydrophilic Intermittent Catheters Hydrophilic catheters have a coating that becomes slippery when activated by water or saline, making insertion smoother and more comfortable. Hydrophilic Coated Intermittent Catheters Key Features: ·Pre-Lubricated Surface: Reduces friction, minimizing irritation and discomfort. ·Sterile Packaging: Often comes with an integrated water packet for convenience. ·Touch-Free Insertion: Many designs include sleeves or grippers to reduce contamination risk. Best For: ·Men prone to urethral irritation or discomfort during insertion. ·Those who require frequent catheterization and prioritize comfort. 4. Pre-Lubricated Intermittent Catheters Similar to hydrophilic catheters, pre-lubricated catheters come ready to use with a lubricating gel already applied. Key Features: ·Ready-to-Use Convenience: No additional preparation or lubrication is required. ·Sterile Packaging: Ensures cleanliness and reduces infection risk. ·Portable: Ideal for travel or on-the-go use. Best For: ·Men who value convenience and quick catheterization. ·Patients with busy lifestyles or limited dexterity. 5. Closed-System Intermittent Catheters A closed-system catheter is a self-contained device with a catheter housed inside a sterile bag. This design minimizes the risk of infection by reducing direct contact with the catheter. Key Features: ·Touch-Free Insertion: A protective sheath or pre-connected bag prevents hand contact with the catheter. ·Integrated Drainage Bag: Eliminates the need for an external urine collection device during catheterization. ·Portable and Discreet: Compact design for use anywhere. Best For: ·Men at high risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs).> ·Patients with limited access to sterile environments. 6. Reusable Intermittent Catheters While most intermittent catheters are single-use, reusable catheters are made from durable materials like silicone, allowing multiple uses when properly cleaned and sterilized. Key Features: ·Cost-Effective: Can be reused multiple times, reducing overall expense. ·Durable Materials: Designed to withstand cleaning and repeated use. ·Eco-Friendly Option: Generates less medical waste compared to disposable catheters. Best For: ·Men seeking an economical or environmentally conscious solution. ·Patients with access to proper cleaning supplies and sterilization tools. 7. Compact or Pocket Intermittent Catheters Compact intermittent catheters are designed for maximum portability and discretion. These catheters are shorter or telescoping, allowing them to fit into small cases or pockets. Key Features: ·Travel-Friendly: Small size makes them easy to carry in a pocket or bag. ·Discreet Packaging: Ideal for use in public or workplace settings. ·Ease of Use: Often pre-lubricated for quick and simple application. Best For: ·Men who travel frequently or lead an active lifestyle. ·Patients who prioritize privacy and discretion. Choosing the Right Intermittent Catheter The best type of intermittent catheter for men depends on several factors: 1.Medical Needs:A straight-tip catheter may suffice for general use, while a coude-tip catheter is better for those with anatomical challenges. 2.Comfort and Convenience:Hydrophilic and pre-lubricated catheters reduce discomfort and simplify insertion. 3.Lifestyle Considerations:Compact and closed-system catheters are ideal for men on the go. 4.Infection Risk:Closed-system and hydrophilic options are recommended for those prone to UTIs.> 5.Frequency of Use:Men who catheterize multiple times daily may benefit from hydrophilic or pre-lubricated catheters to minimize irritation. Working with Intermittent Catheter Suppliers Accessing high-quality catheters from trusted suppliers ensures comfort, safety, and reliability. Look for suppliers offering: ·A variety of catheter types and sizes. ·Educational resources and customer support. ·Discreet shipping options for privacy. Popular brands like Coloplast, Hollister, and Bard provide advanced intermittent catheter solutions tailored to individual needs. Conclusion Intermittent catheters for men come in diverse styles to address unique medical conditions, comfort levels, and lifestyle requirements. From the simplicity of straight-tip catheters to the advanced design of hydrophilic and closed-system options, there's a catheter for every situation. Collaborating with healthcare providers and choosing reliable suppliers ensures the best outcomes, empowering men to manage their urinary health with confidence.
View More + -
26 Nov 2024
The answer is YES, but it depends on the specific circumstances. Due to the shorter and straighter nature of the female urethra, most cases do not require a Coudé catheter, as standard catheters are often sufficient. However, in situations such as urethral strictures, abnormal urethral openings, or complex anatomical structures, a Coudé catheter might be a more suitable choice for female patients. About female coude catheter, you can know more information here.v What Is a Coudé Catheter? A Coudé catheter features a unique curved tip (typically angled at the 12 o'clock position), designed to navigate obstructions or narrow areas in the urethra. Compared to standard straight catheters, the Coudé catheter provides greater comfort and is better suited for challenging clinical scenarios. How Does It Differ From Standard Catheters? Standard catheters are straight and are generally appropriate for most patients without urethral abnormalities. However, they may not easily bypass obstructions or other structural challenges. The curved tip of a Coudé catheter reduces friction and trauma to the urethral walls, making it a preferred choice in more complex situations. While primarily used in male patients, it can also be advantageous for certain female patients. Is It Safe to Use a Coudé Catheter on Female Patients? Yes, Coudé catheters are safe for female patients, but their application should be determined by a healthcare professional when using. Because the female urethra is shorter and straighter, a standard catheter is sufficient in most cases. However, in specific situations such as urethral strictures, abnormal urethral openings, or complex anatomical conditions, a Coudé catheter may be a greater option. When Is a Coudé Catheter Recommended for Female Patients? Generally, female patients have a broader selection of catheter options. But in the following cases, Coudé catheters are a safer and more comfortable choice: 1. Urethral Strictures: When strictures caused by trauma, surgery, or illness make the urethra narrow, a Coudé catheter can bypass the obstruction more easily. 2. Abnormal Urethral Anatomy: If the urethral opening is in an unusual position or the anatomy is otherwise complex, standard catheters may not work effectively, making the Coudé catheter a better alternative. 3. Post-Surgical Cases: Following bladder neck or urethral surgeries, irregularities in the urethra might require the flexibility of a Coudé catheter. 4. Chronic Urinary Retention: For patients needing frequent catheterization, a Coudé catheter can reduce the risk of urethral trauma. How to Properly Insert a Coudé Catheter for Female Patients 1. Preparation and Cleaning Wash hands thoroughly and wear sterile gloves. Prepare lubricant, a sterile catheter, and a urine collection bag. 2. Patient Positioning Position the patient lying on her back with knees slightly bent and legs apart to expose the urethral opening. 3. Cleanse the Urethral Area Use sterile swabs to clean the urethral opening and surrounding area, wiping from the inside out to reduce infection risk. 4. Lubricate the Catheter Apply a sterile lubricant to the catheter tip to minimize friction during insertion. 5. Insert the Catheter Gently insert the catheter with the curved tip pointing upward (12 o'clock position). Move slowly and avoid forcing it if resistance is encountered. Once the catheter reaches the bladder, urine will flow out, indicating successful insertion. 6. Secure the Catheter If an indwelling catheter is required, inflate the retention balloon to secure it in place. 7. Monitor and Record Observe the urine output and record the volume to evaluate the effectiveness of the procedure. Potential Risks and Precautions for Using a Coudé Catheter on Women While Coudé catheters offer unique advantages, they also carry potential risks. Proper precautions should be taken to mitigate these risks: 1. Infection Risk Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are the most common complication. Strict adherence to aseptic techniques and regular catheter replacement are essential to minimize this risk. 2. Urethral Trauma Improper insertion or forcing the catheter can cause damage to the urethral walls, leading to bleeding or injury. Always proceed gently and stop if resistance is encountered. 3. Urethral Spasms or Discomfort Some patients may experience spasms or discomfort during insertion. Consider consulting a doctor about using a local anesthetic if needed. 4. Complications of Long-Term Use Prolonged catheterization may lead to urethral inflammation or stone formation. Periodic assessment of catheter necessity and timely replacement are crucial. If any issues happened, must consult your healthcare provider. Alternatives to Coudé Catheters for Female Patients In cases where a Coudé catheter may not be suitable, consider the following alternatives 1. Standard Straight Catheters Good choice for patients without obstructions or anatomical abnormalities. 2. Silicone Catheters Made from soft, hypoallergenic material, these are suitable for patients with latex allergies. 3. Intermittent Catheterization Periodic insertion can reduce the risk of infection compared to an indwelling catheter. 4. Surgical Intervention For severe obstructions or structural abnormalities, surgery may offer a long-term solution. Conclusion Coudé catheters adopt a unique curved-tip design, good for managing urinary obstructions. Also, female patients can benefit from it sometimes. For example, Bever Medical Coudé catheters are made of DEHP-free PVC material, ensuring an optimal balance of flexibility and comfort to facilitate smooth insertion while reducing the risk of bacterial growth. Using a Coudé catheter must adhere to aseptic techniques and proper insertion methods. As an OE supplier, Bever Medical is committed to providing high-quality continence care products and solutions tailored to meet diverse patient needs. If you don't know the right catheter type, you should follow the doctor’s suggestion.
View More + -
30 Nov 2024
A Coude catheter is a specialized type of urinary catheter that is particularly useful for patients experiencing anatomical obstructions in the urinary tract. Unlike standard straight catheters, which feature a simple tubular design, Coude catheters are characterized by their curved or angled tip. This unique design helps to navigate the catheter past obstacles like an enlarged prostate or urethral strictures, which can make conventional catheterization difficult or impossible. In this article, we will explore the design features of Coude catheters, their clinical applications, and the benefits they offer to both healthcare providers and pat Design Features of Coude Catheters Curved Tip The most distinctive feature of the Coude catheter is its curved or angled tip. The curve is typically more pronounced than that of a standard catheter, which helps it navigate through challenging anatomical structures. The curvature of the tip can vary from a slight bend to a more acute angle, depending on the specific needs of the patient and the nature of the obstruction. The curvature allows the catheter to bypass areas of the urethra that may be blocked or narrowed, such as an enlarged prostate or a urethral stricture. Materials Coude catheters are made from various materials, each with its own set of advantages. The most common materials used are: Latex: Latex catheters are soft and flexible but may cause allergic reactions in some patients. Silicone: Silicone catheters are more hypoallergenic and have a smoother surface, reducing the risk of irritation and infection. They are commonly used for long-term catheterization. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): PVC catheters are durable and are often used for short-term catheterization. Male Coude Tip Intermittent Catheters Some high-performance Coude catheters are coated with hydrophilic materials. These coatings, when activated with water or saline, create a slippery surface, making the catheter easier to insert and reducing friction, thereby minimizing trauma to the urethra. Sizes and Flexibility Coude catheters come in a wide range of sizes, typically measured using the French scale (Fr). This scale ranges from small (e.g., 6Fr) to large (e.g., 24Fr or more) diameters. The flexibility of the catheter is an important design consideration. While some Coude catheters are designed to be stiff for better control during insertion, others are more flexible to accommodate various anatomical conditions and patient preferences. Graduated Markings Many Coude catheters include graduated markings along the shaft, which help healthcare providers measure the depth of insertion and ensure accurate placement. These markings are useful for both short-term catheterization and long-term use. Insertion Sleeve Some Coude catheters come with an insertion sleeve, which helps to minimize handling and contamination of the catheter. The sleeve also assists in achieving proper orientation of the curved tip, ensuring smoother insertion. Clinical Applications of Coude Catheters Coude catheters are primarily used in patients who experience difficulties with conventional straight catheters due to anatomical obstructions or other issues that affect the urethra. Below are some of the most common clinical situations where Coude catheters are used: 1. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Problem: Benign prostatic hyperplasia, or an enlarged prostate, is a common condition in older men. The enlarged prostate can obstruct the urethra, making it difficult or even impossible for a straight catheter to pass through. Solution: The curved tip of the Coude catheter helps bypass the enlarged prostate, allowing the catheter to reach the bladder more easily. This makes the Coude catheter particularly useful for patients with urinary retention due to BPH. 2. Urethral Strictures Problem: Urethral strictures are caused by scarring or narrowing of the urethra, which can occur due to trauma, infection, or previous surgeries. The narrowing makes it difficult for a straight catheter to pass through the urethra. Solution: The angled design of the Coude catheter enables it to navigate past these strictures. The catheter's tip is designed to follow the natural curve of the urethra, helping to minimize the risk of injury and ensuring more successful catheterization. 3. Post-Surgical Urological Care Problem: After urological surgeries such as prostatectomy, bladder surgery, or pelvic surgeries, patients may experience temporary or permanent anatomical changes that make catheterization more difficult. Solution: For these patients, a Coude catheter can be a valuable tool for managing urinary retention or incontinence during the post-operative recovery period. Its curved tip helps avoid trauma to delicate tissues and allows for easier insertion through areas that may have been affected by surgery. 4. Spinal Cord Injury and Neurological Disorders Problem: Patients with spinal cord injuries, multiple sclerosis, or other neurological conditions may have difficulty with bladder control. These patients may also have changes in their urethral anatomy, which makes catheterization challenging. Solution: Coude catheters are often used for patients with neurological conditions. The curved tip aids in intermittent catheterization for individuals with limited sensation or control over their urinary tract, helping to maintain proper bladder function and reduce the risk of infection. 5. Congenital or Anatomical Abnormalities Problem: In some patients, especially children, congenital or anatomical abnormalities may cause the urethra to bend or narrow, making catheterization challenging. Solution: The Coude catheter can be used to navigate around these abnormalities, ensuring safe and effective catheter insertion. This makes it an ideal choice for pediatric patients who may require frequent catheterization due to neurogenic bladder or other conditions. Benefits of Coude Catheters Easier Insertion in Challenging Anatomies: The most significant advantage of the Coude catheter is its ability to navigate past obstructions, whether from an enlarged prostate, urethral strictures, or anatomical variations. This provides a more effective solution when a straight catheter cannot be used. Reduced Risk of Urethral Trauma: The design of the Coude catheter helps minimize the risk of trauma during insertion, which is particularly important for patients with sensitive or compromised urethral tissue. Improved Patient Comfort: Many patients find that the Coude catheter is more comfortable than a straight catheter, especially when dealing with obstructions. The catheter's design allows for easier insertion, reducing pain and discomfort. Minimized Complications: Because Coude catheters are designed to avoid trauma and reduce friction during insertion, they can help minimize complications like urethral injury and infection. Improved Success Rate: For patients with difficult-to-navigate anatomical structures, Coude catheters offer a higher success rate in bladder catheterization, helping to maintain better urinary function and reduce the need for more invasive procedures. Challenges and Considerations While Coude catheters offer many benefits, there are also challenges and considerations that must be kept in mind: Proper Insertion Technique: The curved tip requires proper alignment and technique during insertion. Inaccurate insertion can cause discomfort or injury to the urethra. Patient Training: Patients who need to use Coude catheters on their own may require training to understand how to orient the catheter properly for successful insertion. Risk of Infection: As with all catheters, there is a risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs). Ensuring proper hygiene, using sterile techniques during insertion, and following guidelines for catheter care are essential in minimizing this risk. Conclusion Coude catheters are essential tools in the management of patients with anatomical obstructions, making them invaluable for individuals with conditions like BPH, urethral strictures, or those recovering from urological surgeries. With advancements in design, materials, and patient comfort features, Coude catheters have evolved from basic models to high-performance options that improve patient outcomes and ease the process of catheterization. By offering greater flexibility, better control, and reduced risk of complications, Coude catheters play a key role in ensuring effective urinary management for a wide range of patients. About BEVER Medical BEVER Medical offers a comprehensive range of continence care products and urological supplies, meticulously designed to address diverse needs with exceptional quality and reliability. Our solutions are crafted with the primary goal of enhancing the quality of life for individuals dealing with incontinence, ensuring optimal comfort, protection, and ease of use. From discreet and absorbent incontinence products to advanced urological devices tailored for various conditions, we focus on innovation and practicality. BEVER Medical is committed to supporting our users with products that are not only functional but also empower them to lead confident and active lives. Each item in our range reflects our dedication to comfort, safety, and improving daily living experiences.
View More +



 English
English